Industry Knowledge
How to Collect Chatbot Training Data for Better CX
Your chatbot can only be as good as the data you have and how well you train it.
With the digital consumer’s growing demand for quick and on-demand services, chatbots are becoming a must-have technology for businesses. In fact, it is predicted that consumer retail spend via chatbots worldwide will reach $142 billion in 2024—a whopping increase from just $2.8 billion in 2019. This calls for a need for smarter chatbots to better cater to customers’ growing complex needs.
The challenge is that developing an effective AI-powered chatbot requires a lot of work—and data. You need to feed it loads of information for it to facilitate realistic and human-like conversations. This is where chatbot training data comes in. Equipped with proper chatbot training data, a chatbot can help you improve operations in a myriad of ways: quicker answer times, increased NPS scores, reduced employee workload, just to name a few.
Related: An Introduction to AI Training Data
What is Chatbot Training Data?
Essentially, chatbot training data allows chatbots to process and understand what people are saying to it, with the end goal of generating the most accurate response. Chatbot training data can come from relevant sources of information like client chat logs, email archives, and website content.
In order to quickly resolve user requests without human intervention, chatbots need to take in a ton of real-world conversational training data samples. Without this data, you will not be able to develop your chatbot effectively. This is why you will need to consider all the relevant information you will need to source from—whether it is from existing databases (e.g., open source data) or from proprietary resources. After all, bots are only as good as the data you have and how well you teach them.
Chatbot Training Basics
If you have started reading about chatbots and chatbot training data, you have probably already come across utterances, intents, and entities. These are basic terms one must know when training chatbots.
- Utterances: Something the user says, like a word or a sentence. (e.g., “time,” or “What is the time?”)
- Intents: The intention of a user’s utterance. This is basically what the user wants to happen as an effect of his or her utterance (e.g., if a person asks “What time is it now,” his or her “intent” is to know the time at that given moment).
- Entities: These are keywords that make the user's intent more clear. For example, with the utterance of “What time is it now,” the entities are “time” and “now.”
How to Train a Chatbot
How much data do you need to train a chatbot?
Training your chatbot with high-quality data is vital to ensure responsiveness and accuracy when answering diverse questions in various situations. The amount of data essential to train a chatbot can vary based on the complexity, NLP capabilities, and data diversity. If your chatbot is more complex and domain-specific, it might require a large amount of training data from various sources, user scenarios, and demographics to enhance the chatbot’s performance. Generally, a few thousand queries might suffice for a simple chatbot while one might need tens of thousands of queries to train and build a complex chatbot.
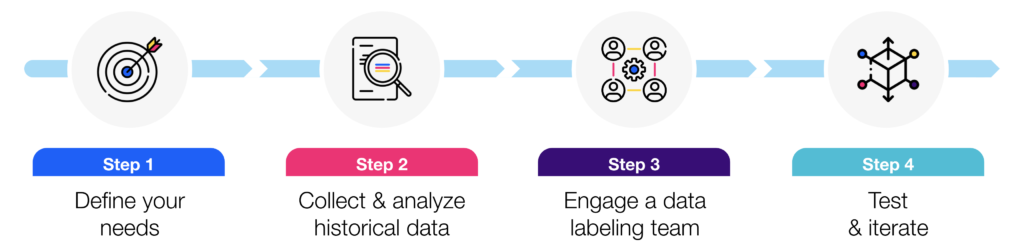
Step 1: Define your needs
Before training your AI-enabled chatbot, you will first need to decide what specific business problems you want it to solve. For example, do you need it to improve your resolution time for customer service, or do you need it to increase engagement on your website? After obtaining a better idea of your goals, you will need to define the scope of your chatbot training project. If you are training a multilingual chatbot, for instance, it is important to identify the number of languages it needs to process.
Step 2: Collect & analyze historical data
The second step would be to gather historical conversation logs and feedback from your users. This lets you collect valuable insights into their most common questions made, which lets you identify strategic intents for your chatbot. Once you are able to generate this list of frequently asked questions, you can expand on these in the next step.
Step 3: Engage a diverse data labeling team
Next, you will need to collect and label training data for input into your chatbot model. This is where working with an experienced data partner will help you immensely—they can support you by collecting all the potential variations of common questions, categorizing utterances by intent and annotating entities. Choose a partner that has access to a demographically and geographically diverse team to handle data collection and annotation. The more diverse your training data, the better and more balanced your results will be.
Step 4: Test & iterate
The process of training your chatbot never really ends. Once your chatbot has been deployed, continuously improving and developing it is key to its effectiveness. Let real users test your chatbot to see how well it can respond to a certain set of questions, and make adjustments to the chatbot training data to improve it over time.
Collect Chatbot Training Data with TaskUs
With over a decade of outsourcing expertise, TaskUs is the preferred partner for human capital and process expertise for chatbot training data.
TaskUs has helped a global technology company facing challenges in audio data collection, variances in local speech, and fluctuating of daily queues for the virtual assistant they were developing—increasing its average accuracy score of less than 64% to 91.7% through data labeling, tagging, and transcription efforts. This allowed the client to provide its customers better, more helpful information through the improved virtual assistant, resulting in better customer experiences.
References

We exist to empower people to deliver Ridiculously Good innovation to the world’s best companies.
Services